
自然资源遥感监测与评估
粤港澳大湾区复杂的自然条件孕育了丰富的自然资源,构成了区域生态安全屏障的重要防线。近几十年来,在气候变化与高强度受人类活动扰动的双重胁迫下,粤港澳大湾区自然资源种类锐减、面积衰减、质量退化趋势明显,亟待开展区域自然资源的动态监测与评估。借助于多源遥感数据,开展空-天-地一体化的自然资源体系构建、自然资源关键生物物理参量提取、自然资源资产评估等议题的研究。形成了百万级别的大湾区农田地块数据集构建、主要经济作物全生长周期动态监测、农田病虫害预警与产量预估等成果。
标志性成果
自然资源监测
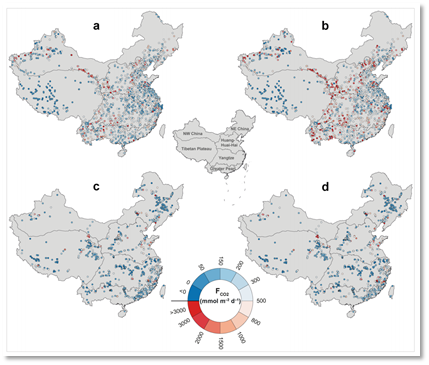
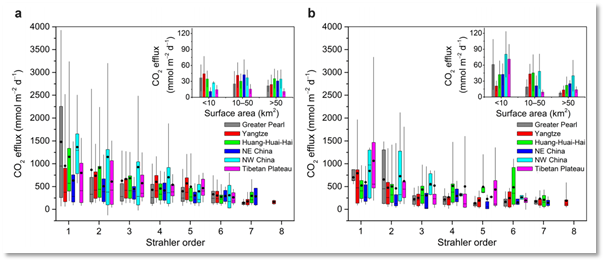
杨现坤副教授在《Nature Communication》上发表了题为“Substantial decrease in CO2 emissions from Chinese inland waters due to global change”的文章,对我国经济高速发展的30年内(1980年代和2010年代)的内陆水体的CO2排放量进行估算,对全球碳循环及未来可持续发展具有重要意义。
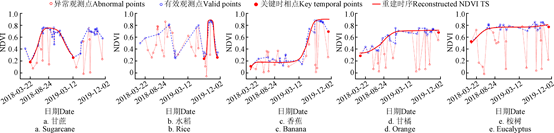
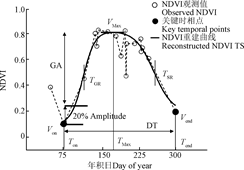
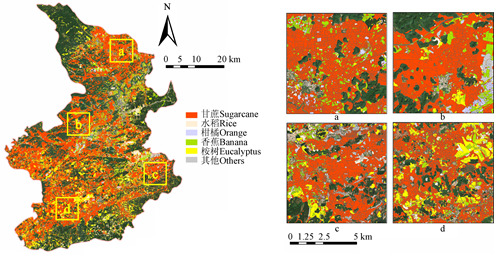
杨颖频博士在《Remote Sensing》和《农业工程学报》期刊上发表题为“Geo-parcel based crop identification by integrating high spatial-temporal resolution imagery from multi-source satellite data”和“时空协同的地块尺度作物分布遥感提取”的文章,基于多源遥感时空协同的思路,以地块为观测尺度融合作物光谱和物候特征,实现地块尺度的作物空间分布精细制图。
自然资源评估
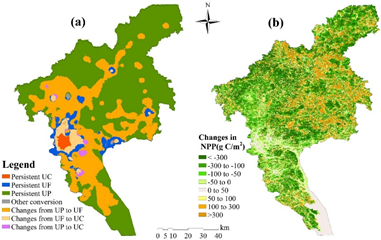
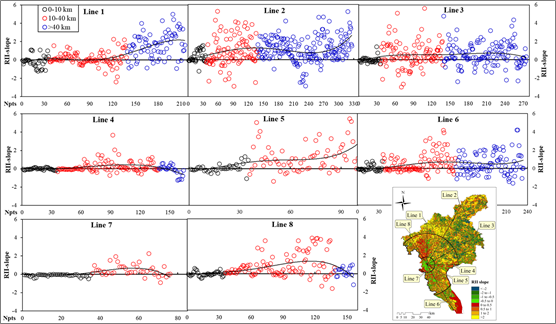
吴艳艳博士分别在《Environmental Science and Pollution Research》和《Environmental Management》上发表题为“Quantitative assessment of human-induced impacts based on net primary productivity in Guangzhou, China”和“Dynamic Changes of Net Primary Productivity and Associated Urban Growth Driving Forces in Guangzhou City, China”的文章,通过提出“相对影响指数”和“城市化特征指数”两个指标定量分析了城市扩张对净初级生产力的影响。成果有助于加深对城市增长模式和相应的城市地理结构变化对城市生态系统影响的认识,为加强城市环境保护和管理提供决策依据。
文章列表:
- Lishan Ran*,David E.Butman,Tom J.Battin,Xiankun Yang*,et al.Substantial decrease in CO2 emissions from Chinese inland waters due to global change. Nature communications.2021,12(1).
- 杨颖频, 吴志峰, 骆剑承*, 等, 2021. 时空协同的地块尺度作物分布遥感提取. 农业工程学报 37, 166-174.
- Yang, Y., Luo, J. *, Huang, Q., et al. 2019. Weighted double-logistic function fitting method for reconstructing the high-quality sentinel-2 NDVI time series data set. Remote Sens. 11, 2342.
- Yang, Y., Huang, Q., Wu, W., et al., 2017. Geo-parcel based crop identification by integrating high spatial-temporal resolution imagery from multi-source satellite data. Remote Sens. 9, 1298.
- Wu Y.Y., Wu Z.F*., Liu X.N. Dynamic changes of net primary productivity and associated urban growth driving forces in Guangzhou city, China. Environmental Management (IF: 2.561, Q2), 2020, 65(6):758-773.
- Yanyan Wu, Zhifeng Wu*. Quantitative assessment of human-induced impacts based on net primary productivity in Guangzhou, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research (IF: 3.056, Q2), 2018, 25(7):11384-11399.
创建: Jan 11, 2022 | 10:02

时空大数据计算与城市感知
城市是自然-经济-社会复杂巨系统的集中体现,是人地系统的关键层级与重要组成。据估计,到2050年,全世界将有70%以上的人口居住于城市地区,其中以印度、中国等发展中国家表现最为明显。由此导致的诸如土地问题、污染问题、城市更新问题等“城市病”已成为制约城市可持续发展、人群生活福祉提升的主要因素。为了更好的应对快速城市化带来的挑战,城市生态与人居环境团队借助时空大数据,通过多视角学习方式融合多源异构数据,实现对城市参与者的全面多维感知;基于大规模出行数据,实现人群出行习惯、出行体验解析;基于大数据智能分析,结合城市发展规律,对城市的基础设施布局和公共资源分配进行智能分析和决策。团队已发表相关领域学术论文20余篇,授权发明专利1项,省部级以上项目资助4项,获得中国地理信息产业协会科技二等奖等奖项4项。
标志性成果:
交通大数据计算:
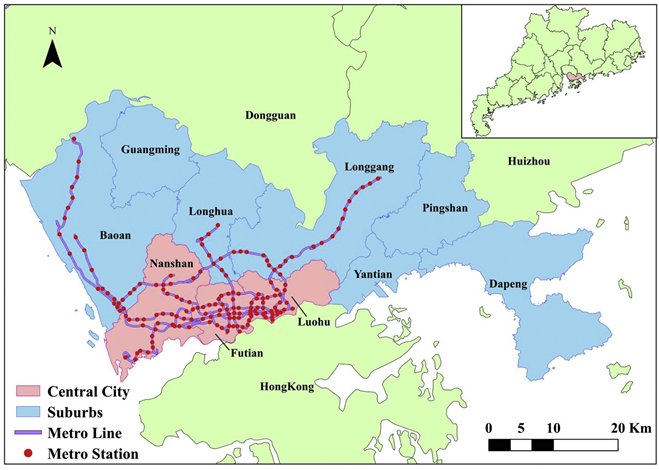
李少英副教授在《Journal of Transport Geography》上发表题为“Inferring the trip purposes and uncovering spatio-temporal activity patterns from dockless shared bike dataset in Shenzhen”的文章,提出了一个基于引力模型和贝叶斯规则的无停靠共享单车用户目的推断框架,并在中国深圳进行了实证。为自行车基础设施规划和无对接共享单车管理提供科学决策。

人群健康暴露风险评估:
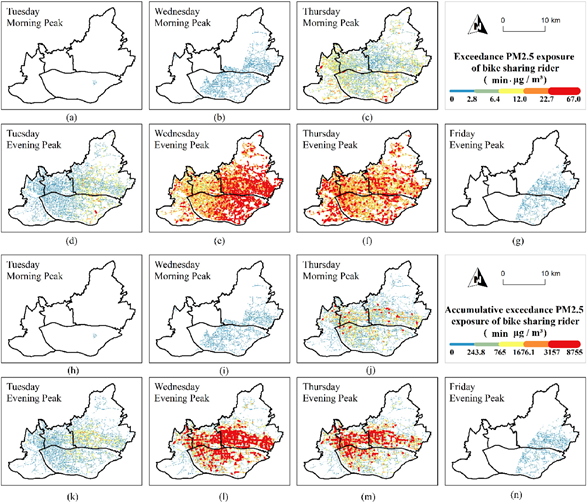
曹峥博士在JCR一区期刊《Environmental Research》上发表题为“Ridership exceedance exposure risk: Novel indicators to assess PM2.5 health exposure of bike sharing riders”的文章,通过开发两个新指标,考察了PM2.5超标对自行车骑行者健康威胁的增加。该研究结果可为制定相关缓解策略提供决策依据,从而实现健康城市的目标。
主要成果列表:
- Li S Y, Zhuang C G, Tan Z Z, Gao F, Lai Z P, Wu Z F*. Inferring the trip purposes and uncovering spatio-temporal activity patterns from dockless shared bike dataset in Shenzhen, China. Journal of Transport Geography, 2021,91:102974.
- Gao F, Li S Y*, Tan Z Z, Wu Z F, Zhang X M, Huang G P, Huang Z W. Understanding the modifiable areal unit problem in dockless bike-sharing usage and exploring the interactive effects of built environment factor. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2021,35(9):1905-1925.
- Zheng Cao, Feng Gao, Shaoying Li*, Zhifeng Wu*, Wenchuan Guan, Hung Chak Ho. Ridership exceedance exposure risk: Novel indicators to assess PM2.5 health exposure of bike sharing riders. Environmental Research, 2021,197:111020.
- Zheng Cao, Zhifeng Wu*, Lin Liu, Yinbiao Chen, Yuxuan Zou. Assessing the relationship between anthropogenic heat release warming and building characteristics in Guangzhou: A sustainable development perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 695.
- 一种人为热增温效应的分析方法、装置及存储介质(ZL201910519181.1),发明专利
创建: Jan 11, 2022 | 10:02

城市生态遥感分析
城市化是人类社会发展的必然趋势,据世界银行统计,2020年全球人口为77.53亿,城市人口为43.52亿,到2050年,城市人口的比例将达到68%。伴随着城市化进程和人类活动强度的加剧,城市生态系统正面临着日益严峻的挑战。及时地开展城市生态的监测并发现所存在的问题,有利于维护城市生态的稳定性并助力可持续发展目标(SDGs)的实现。为了积极响应SDGs目标,城市生态与人居环境团队借助多源遥感数据,收集城市生态系统的专题信息,实现对城市生态过程和环境机制的综合表征,包括:联合卫星与地表传感网的多维城市热环境感知,为改善城市热岛效应提供理论支持;基于城市水文传感大数据,结合城市地表景观格局,对城市地表径流与内涝风险进行智能分析和决策;基于昼夜遥感协同的人类足迹与区域生境的动态追踪,有助于揭示人类活动对生境状况的作用。已发表相关领域学术论文20余篇,授权发明专利1项,省部级以上项目资助20余项,获得广东省科技进步奖一等奖、华夏建设科学技术奖一等奖等奖项。
标志性成果:
城市热环境与景观分析:
郭冠华副教授在JCR Q1期刊《Landscape and Urban Planning》上发表题为“Impacts of urban biophysical composition on land surface temperature in urban heat island clusters”的文章,通过引入了一种创新的集成方法,将面向对象的图像分割与空间自相关的局部指标 (LISA) 相结合,从LST 图像中提取UHI簇,所建立回归树模型能够有效地检测LST与生物物理成分之间的非线性关系。该研究结果有助于更全面的理解城市景观配置与热环境的关系,可为缓解城市热岛效应提供支持。
城市内涝模拟评估:
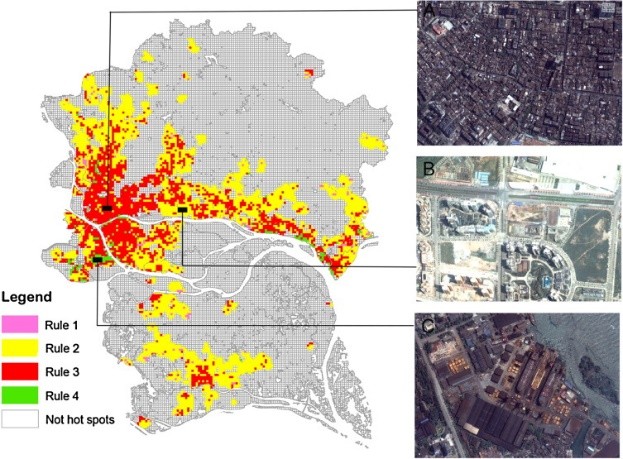
张棋斐博士生在JCR Q1期刊《Science of The Total Environment》上发表题为“Explicit the urban waterlogging spatial variation and its driving factors: The stepwise cluster analysis model and hierarchical partitioning analysis approach”的文章,提出了一种在通用框架内结合逐步聚类分析模型(SCAM)和层次划分分析(HPA)的新方法,并通过逻辑回归、人工神经网络和支持向量机验证其适用性。该研究本有望为SCAM和HPA在城市内涝模拟与评估中的进一步应用提供有益信息,为内涝风险防范带来启示。
地表光污染追踪:
郑子豪博士在JCR Q1期刊《Global Environmental Change》上发表题为“Africa's protected areas are brightening at night: A long-term light pollution monitor based on nighttime light imagery”的文章,使用统一的多传感器NTL数据对非洲保护区的光污染进行了长期(1992-2018)的监测和评估,并探讨了人类活动强度对保护区内光污染的最大作用距离。该研究为理解保护区内的光污染模式提供了新的方法,对未来的保护区规划具有重要参考价值。
主要成果列表:
- Guo, G., Wu, Z., Xiao, R., Chen, Y., Liu, X., & Zhang, X. (2015). Impacts of urban biophysical composition on land surface temperature in urban heat island clusters. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2015,135:1-10.
- Guo, G., Wu, Z., & Chen, Y. Evaluation of spatially heterogeneous driving forces of the urban heat environment based on a regression tree model.Sustainable Cities and Society, 2020,54.
- Zhang, Q., Wu, Z., Guo, G., Zhang, H., & Tarolli, P.. Explicit the urban waterlogging spatial variation and its driving factors: The stepwise cluster analysis model and hierarchical partitioning analysis approach. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 763:143041.
- Zhang, Q., Wu, Z., & Tarolli, P.. Investigating the Role of Green Infrastructure on Urban WaterLogging: Evidence from Metropolitan Coastal Cities. Remote Sensing, 2020,13(12):2341.
- Zheng, Z., Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Guo, G., Cao, Z., Yang, Z., & Marinello, F.. Africa's protected areas are brightening at night: A long-term light pollution monitor based on nighttime light imagery. Global Environmental Change, 2021,69:102318.
- Zheng, Z., Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Guo, C., & Marinello, F. Instability of remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) and its improvement for time series analysis. Science of The Total Environment, 2022,814:152595.
- 一种城市热岛范围的提取方法及装置(ZL201810056935.X),发明专利
创建: Jan 11, 2022 | 10:01












