时空大数据计算与城市感知
城市是自然-经济-社会复杂巨系统的集中体现,是人地系统的关键层级与重要组成。据估计,到2050年,全世界将有70%以上的人口居住于城市地区,其中以印度、中国等发展中国家表现最为明显。由此导致的诸如土地问题、污染问题、城市更新问题等“城市病”已成为制约城市可持续发展、人群生活福祉提升的主要因素。为了更好的应对快速城市化带来的挑战,城市生态与人居环境团队借助时空大数据,通过多视角学习方式融合多源异构数据,实现对城市参与者的全面多维感知;基于大规模出行数据,实现人群出行习惯、出行体验解析;基于大数据智能分析,结合城市发展规律,对城市的基础设施布局和公共资源分配进行智能分析和决策。团队已发表相关领域学术论文20余篇,授权发明专利1项,省部级以上项目资助4项,获得中国地理信息产业协会科技二等奖等奖项4项。
标志性成果:
交通大数据计算:
李少英副教授在《Journal of Transport Geography》上发表题为“Inferring the trip purposes and uncovering spatio-temporal activity patterns from dockless shared bike dataset in Shenzhen”的文章,提出了一个基于引力模型和贝叶斯规则的无停靠共享单车用户目的推断框架,并在中国深圳进行了实证。为自行车基础设施规划和无对接共享单车管理提供科学决策。
人群健康暴露风险评估:
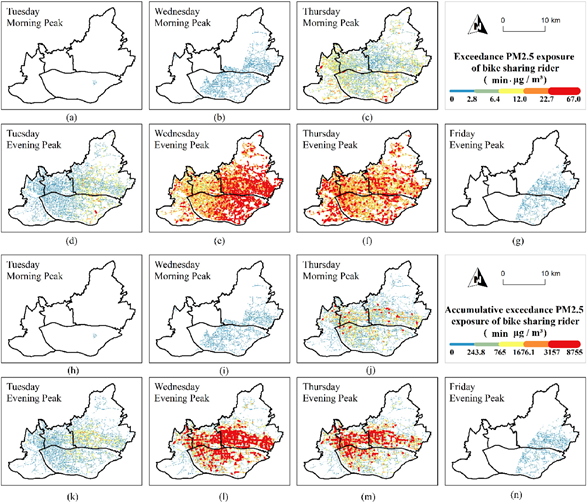
曹峥博士在JCR一区期刊《Environmental Research》上发表题为“Ridership exceedance exposure risk: Novel indicators to assess PM2.5 health exposure of bike sharing riders”的文章,通过开发两个新指标,考察了PM2.5超标对自行车骑行者健康威胁的增加。该研究结果可为制定相关缓解策略提供决策依据,从而实现健康城市的目标。
主要成果列表:
- Li S Y, Zhuang C G, Tan Z Z, Gao F, Lai Z P, Wu Z F*. Inferring the trip purposes and uncovering spatio-temporal activity patterns from dockless shared bike dataset in Shenzhen, China. Journal of Transport Geography, 2021,91:102974.
- Gao F, Li S Y*, Tan Z Z, Wu Z F, Zhang X M, Huang G P, Huang Z W. Understanding the modifiable areal unit problem in dockless bike-sharing usage and exploring the interactive effects of built environment factor. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2021,35(9):1905-1925.
- Zheng Cao, Feng Gao, Shaoying Li*, Zhifeng Wu*, Wenchuan Guan, Hung Chak Ho. Ridership exceedance exposure risk: Novel indicators to assess PM2.5 health exposure of bike sharing riders. Environmental Research, 2021,197:111020.
- Zheng Cao, Zhifeng Wu*, Lin Liu, Yinbiao Chen, Yuxuan Zou. Assessing the relationship between anthropogenic heat release warming and building characteristics in Guangzhou: A sustainable development perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 695.
- 一种人为热增温效应的分析方法、装置及存储介质(ZL201910519181.1),发明专利